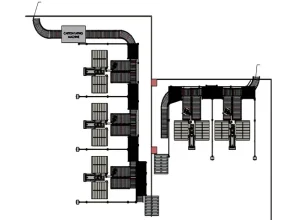
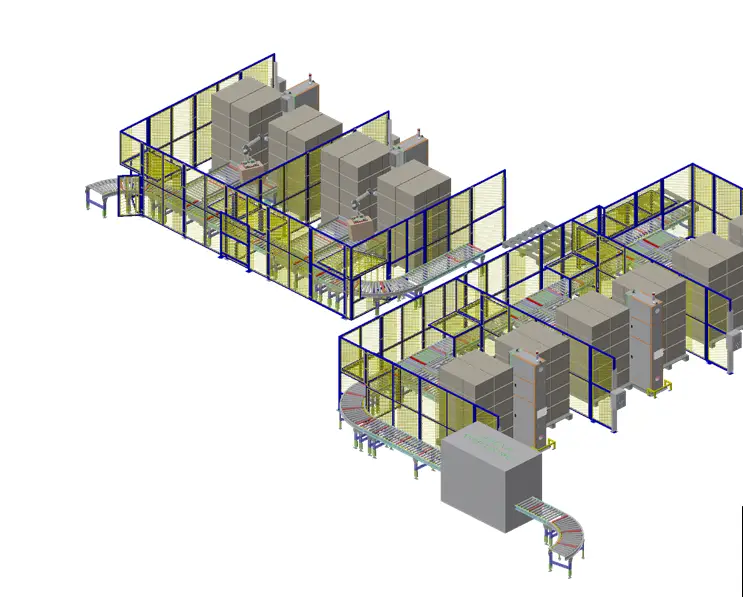
End of Line Automation
End of Line Automation
This term typically refers to the final stages of a production line or manufacturing process, where automation systems are implemented to perform various tasks related to the packaging, inspection, and sorting of finished products. End-of-Line Automation aims to optimize the final stages of production, ensuring that products are efficiently packaged, checked for quality, and prepared for distribution.
Key components of End of Line Automation may include robotic systems for palletizing, automated packaging machinery, quality control systems, labeling machines, and conveyor systems for the
transportation of finished goods. The goal is to streamline the last steps of the manufacturing process, reduce manual labor, enhance accuracy, and improve overall efficiency in preparing products for shipment.

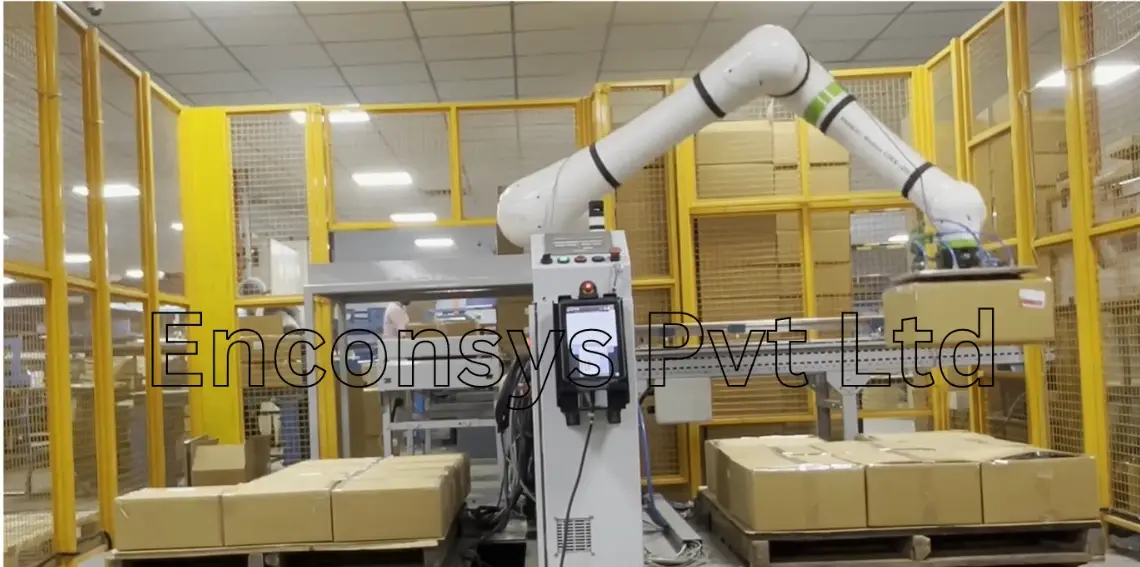
- Palletizing is a material handling operation that involves arranging and stacking items or products on a pallet in a specific and organized manner. The goal of palletizing is to efficiently use the available space on the pallet while ensuring stability and ease of handling during transportation, storage, or distribution.
In industrial and warehouse settings, palletizing operations are often automated using robotic systems or specialized machinery. These systems are programmed to pick up items from a conveyor belt or another source and place them on a pallet according to a predetermined pattern. The pattern may be optimized based on factors such as the size and weight of the items, as well as the desired stability of the palletized load.

- A conveyor is a mechanical system or device used to transport goods, materials, or objects from one location to another within a defined path. It consists of a continuous belt, chain, or other moving surface that supports and moves items along a predefined route. Conveyors are commonly used in various industries, such as manufacturing, mining, agriculture, and logistics, to streamline and automate the process of moving goods efficiently. They can be configured in different shapes and sizes to accommodate the specific needs of the application, and they play a crucial role in enhancing productivity and reducing manual labor in material handling processes.
Sorting operations play a pivotal role in optimizing various industrial processes, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring smooth workflow management. In industries, such as manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain, sorting is fundamental for maintaining organized inventories. Warehouses often employ sorting to categorize products based on factors like SKU, type, or expiration date, facilitating streamlined retrieval and inventory tracking. Additionally, sorting is essential in quality control processes, where manufactured goods undergo inspection and are sorted based on their quality levels for further actions like rework or rejection.In these diverse industrial settings, sorting operations contribute to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved overall productivity. Advanced technologies, such as conveyor systems and robotic sorting, are often integrated to automate and further enhance the speed and accuracy of sorting processes, reflecting the continuous evolution of industrial practices.

- A transfer system in industries refers to a mechanism or set of technologies designed to move goods, materials, or products from one location to another within a production facility or between different stages of a manufacturing process. These systems are essential for streamlining production, increasing efficiency, and reducing manual handling. Various types of transfer systems are employed in different industries, each tailored to specific requirements.

- Auto case filling in industries refers to the automated process employed in manufacturing, packaging, or logistics to fill containers or cases with products, optimizing efficiency and reducing manual labor. The system typically begins with automated sorting based on criteria like size or weight, ensuring accurate matching of items with designated cases. Precision measurement, often utilizing sensors, guarantees the correct quantity of products per case. Robotic pick-and-place operations contribute to the speed and precision of the process, while conveyor systems facilitate a continuous flow from sorting to auto case filling stations. Automated sealing and labeling mechanisms maintain product integrity and support inventory management. Integration with control systems, often utilizing programmable logic controllers, ensures synchronization and efficiency. Quality control measures, including sensors, detect irregularities for quick adjustments. Data logging and reporting features enable operators to monitor productivity and make informed decisions for process improvement. This holistic approach to auto case filling enhances overall productivity and accuracy in various industries, including manufacturing, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and logistics.